Introduction
Keeping up with an industry as fast-moving as AI is a tall order. So until an AI can do it for you, here’s a handy roundup of recent stories in the world of machine learning, along with notable research and experiments we didn’t cover on their own.
Labeling and Annotation Startups in the AI Industry
This week in AI, I’d like to turn the spotlight on labeling and annotation startups — startups like Scale AI, which is reportedly in talks to raise new funds at a $13 billion valuation. Labeling and annotation platforms might not get the attention flashy new generative AI models like OpenAI’s Sora do. But they’re essential. Without them, modern AI models arguably wouldn’t exist.
The Importance of Data Annotation in AI Training
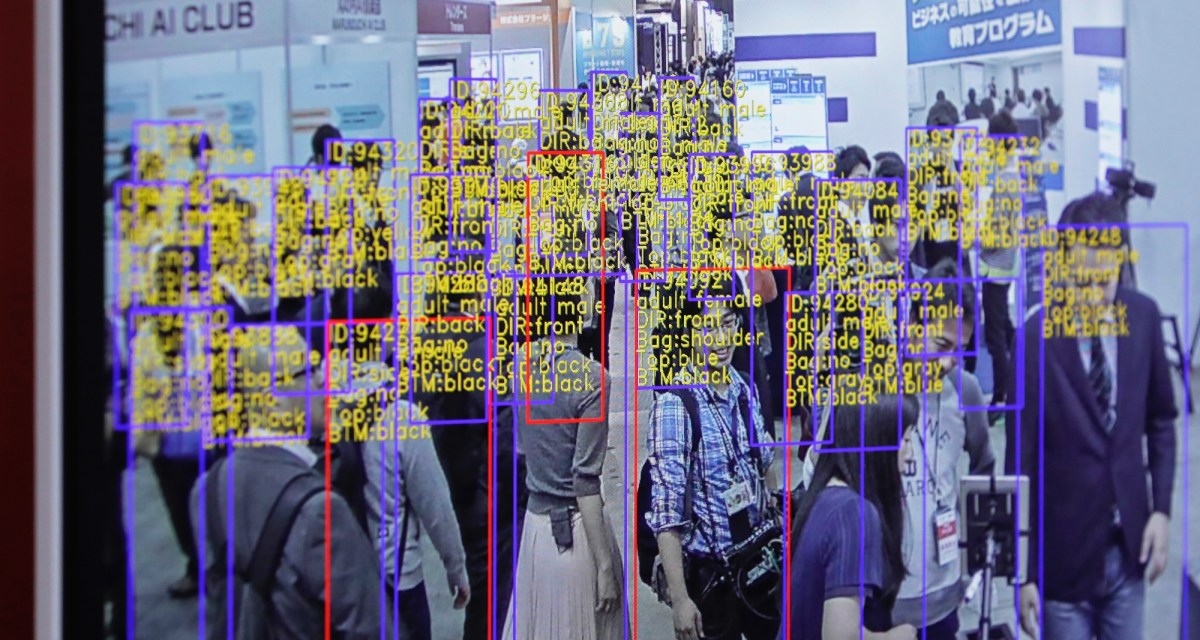
The data on which many models train has to be labeled. Why? Labels, or tags, help the models understand and interpret data during the training process. For example, labels to train an image recognition model might take the form of markings around objects, “bounding boxes” or captions referring to each person, place or object depicted in an image.
Challenges Faced by Data Annotators
The accuracy and quality of labels significantly impact the performance — and reliability — of the trained models. And annotation is a vast undertaking, requiring thousands to millions of labels for the larger and more sophisticated data sets in use.
Ethical Concerns in Annotation and Labeling Industry
So you’d think data annotators would be treated well, paid living wages and given the same benefits that the engineers building the models themselves enjoy. But often, the opposite is true — a product of the brutal working conditions that many annotation and labeling startups foster.
AI Stories of Note
Here are some other AI stories of note from the past few days:
-
- OpenAI builds a voice cloner: OpenAI is previewing a new AI-powered tool it developed, Voice Engine, that enables users to clone a voice from a 15-second recording of someone speaking. But the company is choosing not to release it widely (yet), citing risks of misuse and abuse.
- Amazon doubles down on Anthropic: Amazon has invested a further $2.75 billion in growing AI power Anthropic, following through on the option it left open last September.
- … (More AI stories listed here)
More Machine Learnings
How’s the weather? AI is increasingly able to tell you this. I noted a few efforts in hourly, weekly, and century-scale forecasting a few months ago, but like all things AI, the field is moving fast.
SEEDS: Scalable Ensemble Envelope Diffusion Sampler
SEEDS uses diffusion to generate “ensembles” of plausible weather outcomes for an area based on the input much faster than physics-based models.
Fujitsu’s Approach to Underwater Imagery Analysis
Fujitsu is applying AI image handling techniques to underwater imagery and lidar data collected by underwater autonomous vehicles to better understand the natural world.
Linear Functions in Large Language Models (LLMs)
Researchers have found that large language models mimic intelligence by using simpler methods like linear functions.
Automated Character Interactions by Disney Research
Disney Research has been exploring automated character interactions, including a paper on extracting phonemes for improved name pronunciation in interactions.
AI and Search Integration
As AI and search overlap more, it’s worth reassessing how these tools are used and whether there are any new risks presented by this integration.
Conclusion
Lastly, as AI and search overlap more and more, it’s worth reassessing how these tools are used and whether there are any new risks presented by this integration.
FAQs
1. What are the key challenges faced by data annotators in the AI industry?
2. How is Fujitsu using AI to analyze underwater imagery?
3. What are some notable AI stories from recent days?
4. Why are labeling and annotation startups crucial for modern AI models?
5. What ethical concerns exist in the annotation and labeling industry?
6. How do linear functions play a role in large language models?
7. What is Disney Research’s approach to automated character interactions?
References: TechCrunch, NY Mag, MIT Tech Review, Google.org, Disney Research, Fujitsu, OpenAI